
 Dr Park lectured in Instructional course of 2011 KAPS Dr Park lectured in Instructional course of 2011 KAPS |
|||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Dr Park lectured in Instructional course for yourng plastic surgeons of 2011 KAPS(Korean Aesthetic Plastic Surgery) Meeting.
His lecture subject was The practical anatomy for breast surgery Object: To obtain anatomic essentials for 1. the bloodless pocket 2. reducing the double bubble appearance. 3. making V-valley and reducing symmastia 4. better shape Introduction Anatomy is fundamentally important in all surgery, so I would like to share practically my experiences in anatomical aspect for the better, consistent and safe results. Bony structure: If the angle of the rib cage at the anterior axillary line is acute, implant tends to move medially. In case of the prominent sternocostal junction, implant tends to move laterally. Anterior convexity of the rib cage affects breast shape and size. Muscular structure: The pectorlis muscle action affects the result in case of submuscular placement. The pushing direction of muscle changes whether muscle cuts or not. Narrow muscle width and sternalis muscle act as a laterally displacing cause. At the second and third costal cartilages, the muscle is thickened and attached more laterally, which is occurred by decussation of muscle fibers. Detachment of muscle origin at this portion is important for better shape, however surgeon should be careful due to perforators. Serratus tends to tether overlying soft tissue, so in case of blindly making pocket with abduction of shoulder, detachment of soft tissue from serratus should be done enough. Fascial system: From superficial to deep layer, superficial layer of superficial fascia, deep layer of superficial fascia, pectoralis fascia(pectoralis major and minor). Breast is located between superficial and deep layer of superficial fascia. Interfascial space is avascular layer, so surgeon should make pocket through interfascial space. Nerves, arteries and veins: The most important nerve is known as the lateral cutaneous branch of the fourth intercostals nerve, however it seems that other nerves may be substitute; especially lateral and anterior branches from the third to the fifth intercostal nerve. In case of transaxillary approach, thoracoepigastric vein should be dealt carefully. As several perforators arise consistently, surgeon can make dry pocket with the intended cauterization. 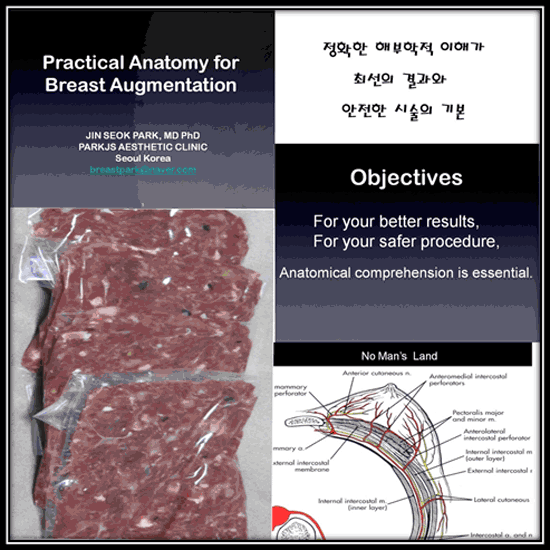 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
 |
|